Chemical bonding and reactions close reading assignment introduces a captivating journey into the realm of chemical interactions, offering a comprehensive exploration of the fundamental principles that govern the formation and behavior of chemical substances. As we delve into this intriguing topic, we will uncover the intricacies of chemical bonding, unravel the dynamics of chemical reactions, and discover the profound applications that shape our world.
Through this close reading assignment, we embark on a quest to unravel the mysteries of chemical bonding, exploring the forces that hold atoms together to form molecules and compounds. We will investigate the properties of different types of bonds, examining how they influence the characteristics of the substances they create.
Chemical Bonding and Reactions
Chemical bonding and reactions are fundamental concepts in chemistry that govern the interactions between atoms and molecules. These processes shape the properties and behavior of matter in our world.
Chemical Bonding
Chemical bonding refers to the forces that hold atoms together to form compounds. The type of bond formed depends on the electronic configurations of the atoms involved.
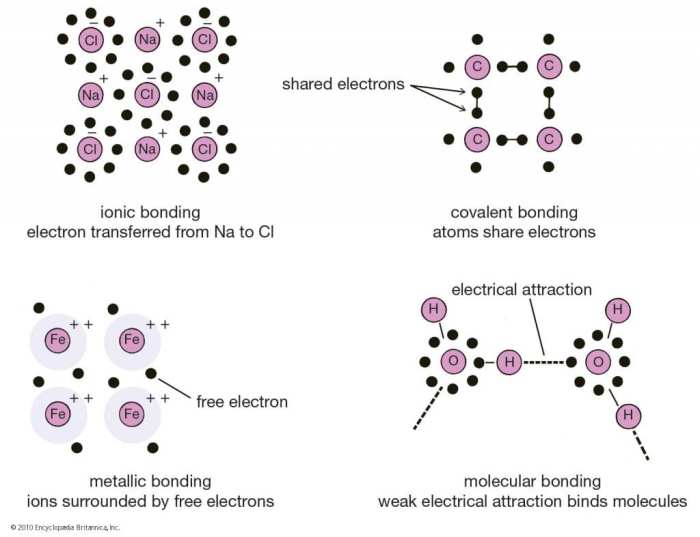
Ionic Bonding
Ionic bonding occurs when one atom transfers electrons to another, resulting in the formation of oppositely charged ions. The electrostatic attraction between these ions holds the compound together. Examples include sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium iodide (KI).
Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons between atoms. This type of bond is typically formed between non-metals. Examples include water (H 2O) and carbon dioxide (CO 2).
Metallic Bonding
Metallic bonding occurs in metals and involves the delocalization of electrons in a “sea” of positive ions. This type of bond results in high electrical and thermal conductivity.
Chemical Reactions
A chemical reaction is a process in which atoms or molecules rearrange themselves to form new substances. Reactions can be classified into various types.
Synthesis Reactions
Synthesis reactions combine two or more reactants to form a single product. For example:
2H 2+ O 2→ 2H 2O
Decomposition Reactions
Decomposition reactions break down a single reactant into two or more products. For example:
2H 2O → 2H 2+ O 2
Single Displacement Reactions
Single displacement reactions involve the replacement of one element in a compound by another element. For example:
Fe + 2HCl → FeCl 2+ H 2
Double Displacement Reactions
Double displacement reactions involve the exchange of ions between two compounds. For example:
NaCl + AgNO 3→ AgCl + NaNO 3
Factors Affecting Chemical Reactions
The rate of a chemical reaction can be influenced by several factors:
Temperature
Increasing temperature generally increases the reaction rate by providing more energy to the reactants.
Concentration
Higher concentrations of reactants lead to a higher probability of collisions, resulting in a faster reaction rate.
Surface Area
Increasing the surface area of reactants increases the number of active sites available for reactions, leading to a faster reaction rate.
Applications of Chemical Bonding and Reactions, Chemical bonding and reactions close reading assignment
Chemical bonding and reactions have numerous applications in various fields:
Medicine
Understanding chemical reactions is crucial for developing drugs, vaccines, and other medical treatments.
Industry
Chemical bonding and reactions are used in the production of plastics, fertilizers, and other industrial materials.
Agriculture
Chemical reactions are essential for photosynthesis, plant growth, and the development of fertilizers.
FAQ: Chemical Bonding And Reactions Close Reading Assignment
What is the difference between covalent and ionic bonds?
Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, while ionic bonds result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, creating charged ions.
How do chemical reactions affect the properties of substances?
Chemical reactions can drastically alter the properties of substances, changing their physical and chemical characteristics, such as their appearance, solubility, and reactivity.
What factors influence the rate of chemical reactions?
Factors such as temperature, concentration, surface area, and the presence of catalysts can significantly impact the rate at which chemical reactions occur.